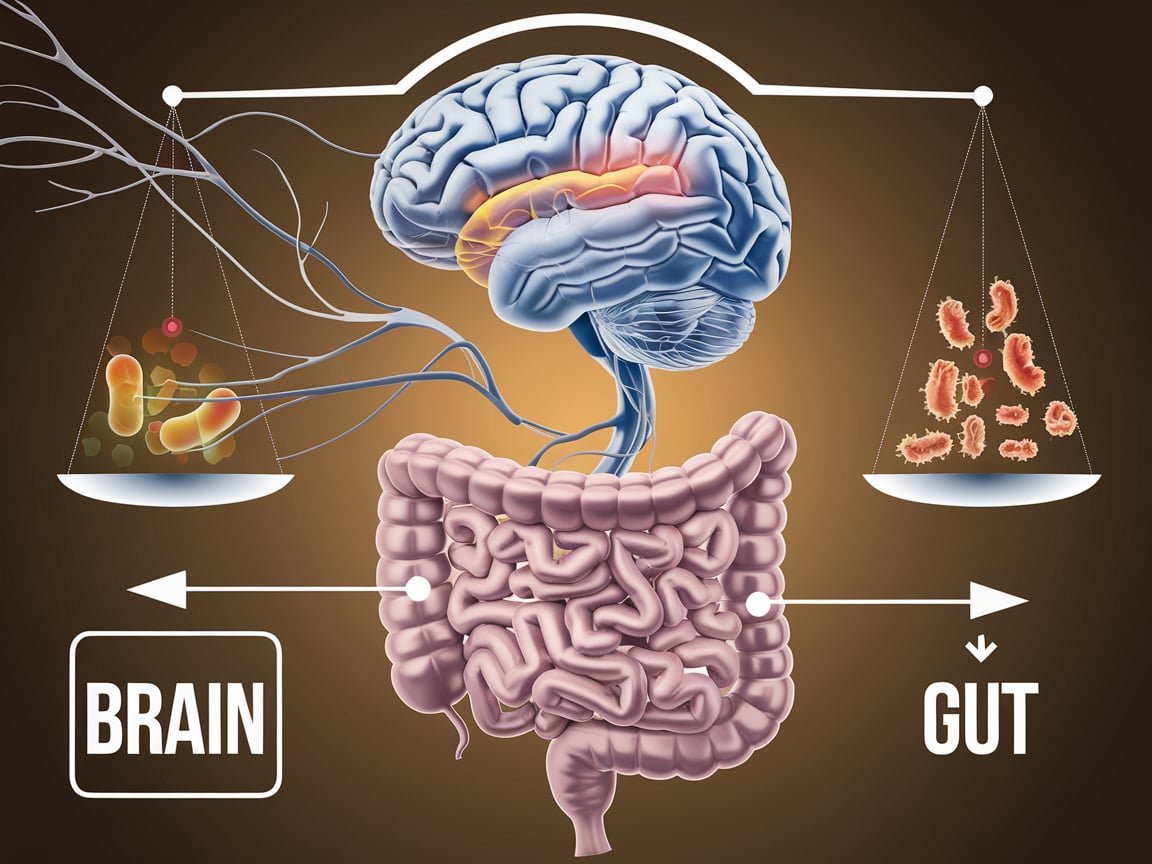
"The Science Behind the Gut-Brain Connection: How Your Diet Impacts Mental Health – Explore the powerful link between your gut and brain, and how what you eat can influence mood, stress, and cognitive function."
Meta Description:
Learn how the gut-brain connection works, how your diet affects your mental health, and what foods can improve your mood and cognitive function. Discover the science behind gut health and mental wellness.
The Science Behind the Gut-Brain Connection: How Your Diet Impacts Mental Health
Our health is a complex network, where everything from diet to lifestyle influences our well-being. One of the most fascinating systems in the body is the gut-brain connection. The gut and the brain are in constant communication, and this connection affects much more than digestion—it plays a significant role in mood, mental health, and cognitive function. The way we care for our gut directly influences how we feel and think.
In this article, we’ll explore how the gut-brain connection works, why a healthy gut is crucial for your mental well-being, and how making smarter dietary choices can lead to better mental health outcomes.
What Is the Gut-Brain Connection?
The gut-brain connection refers to the two-way communication between your digestive system and your brain. This connection occurs through several pathways, including the vagus nerve, a direct communication line that connects the brain and the gut. Research has shown that the microbes in the gut—collectively known as the gut microbiome—play a major role in this communication by producing neurotransmitters like serotonin and dopamine, which regulate mood and emotional responses.
The gut-brain connection is not just a one-way street; it’s a dynamic and ongoing interaction where the state of your gut can significantly impact your mental health.
How the Gut Affects Your Brain
The gut-brain connection is deeply rooted in the biochemical signals that the gut microbiota sends to the brain. It is through these pathways that the gut can influence mood, cognitive function, and even mental health conditions such as depression and anxiety.
- Neurotransmitter Production: A large portion of serotonin, often referred to as the “feel-good” neurotransmitter, is produced in the gut. This highlights just how interconnected the gut-brain connection is with emotional well-being. A healthy gut produces the necessary chemicals to help maintain a positive mood.
- Inflammation and Mood Disorders: Chronic inflammation is a known contributor to mental health issues like depression and anxiety. The gut-brain connection can influence systemic inflammation, and an imbalance in gut bacteria can increase inflammation, leading to mood disturbances and stress.
- Cognitive Function and Memory: The health of your gut has been shown to affect cognitive abilities, such as memory and learning. A balanced gut microbiome can promote the growth of new neurons, which may improve memory and protect against cognitive decline.
- Stress Response: The gut-brain connection also regulates how the body responds to stress. Disruptions in the gut microbiome can lead to increased stress levels, which can, in turn, impact brain function. The vagus nerve is a key player in this, transmitting signals of stress between the brain and the gut.
The Role of Diet in Gut Health
Your diet plays a pivotal role in maintaining a healthy gut microbiome. The foods you eat directly impact the diversity and balance of gut bacteria, which in turn affects your gut-brain connection. Research shows that diets rich in fiber, fermented foods, and healthy fats are beneficial for both gut and brain health.
Foods That Promote Gut Health and Mental Wellness
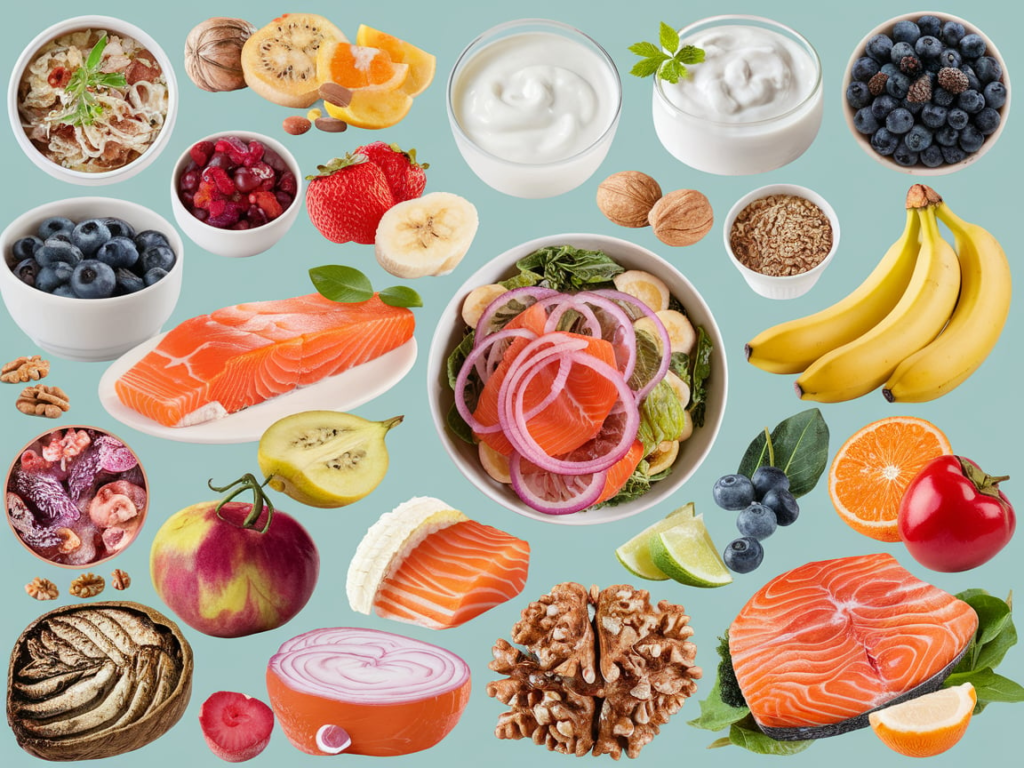

- Prebiotics: Prebiotics are compounds found in certain foods that help nourish beneficial gut bacteria. These foods support the gut-brain connection by encouraging the growth of healthy microbes. Foods rich in prebiotics include:
- Bananas
- Garlic
- Onions
- Asparagus
- Oats
- Probiotics: Probiotics are live bacteria found in fermented foods that directly benefit the gut microbiome. Foods like:
- Yogurt
- Sauerkraut
- Kimchi
- Kefir
- Miso
- Omega-3 Fatty Acids: Omega-3 fatty acids found in foods like salmon, mackerel, and walnuts have anti-inflammatory effects that support both the gut and brain. These healthy fats are particularly important for reducing brain inflammation, which plays a role in mental health conditions.
- Polyphenols: Foods rich in antioxidants, such as berries, dark chocolate, and green tea, promote gut health by supporting the growth of beneficial bacteria. They also reduce oxidative stress, which has been linked to mood disorders and cognitive decline.
- Fermented Foods: Fermented foods, as mentioned earlier, contain beneficial bacteria that can significantly enhance the gut-brain connection. These foods are particularly important for gut healing, improving digestion, and restoring microbial balance.
Foods That Harm Gut Health
Just as certain foods can benefit the gut, others can disrupt the gut-brain connection and lead to mental health issues. Here are some foods to avoid:
- Highly Processed Foods: Foods high in artificial additives and unhealthy fats can disrupt the balance of gut bacteria, leading to inflammation and negatively affecting mental health.
- Excessive Sugar: High sugar intake is known to promote the growth of harmful bacteria in the gut and disrupt the balance of the microbiome, leading to increased inflammation and stress.
- Artificial Sweeteners: Research has shown that artificial sweeteners can negatively impact gut microbiota, affecting mental health by promoting an imbalance in bacteria.
How the Gut-Brian Connection Impacts Mental Health
The gut-brain connection plays a crucial role in mental health conditions like depression, anxiety, and even neurodegenerative diseases. Imbalances in the gut microbiome can exacerbate these conditions, while improving gut health can help alleviate symptoms.
Depression and the Gut-Brain Connection
Depression is one of the most widely studied mental health conditions related to the gut-brain connection. Researchers have found that people with depression often have an imbalanced microbiome, and restoring gut health through diet and probiotics can help alleviate symptoms. By supporting the gut-brain connection, individuals may experience improved mood and cognitive function.
Anxiety and Stress
Anxiety disorders are often linked to dysbiosis, an imbalance of the gut microbiome. Studies show that people with anxiety have a higher prevalence of gut-related issues, and improving gut health can reduce feelings of anxiety. Probiotics and prebiotics play a key role in restoring balance and supporting the gut-brain connection.
Cognitive Decline and Alzheimer’s Disease
Research suggests that the gut-brain connection could also be involved in neurodegenerative diseases like Alzheimer’s. An unhealthy gut may contribute to inflammation in the brain, leading to cognitive decline. By supporting gut health, it’s possible to protect against memory loss and other symptoms of cognitive decline.
How to Support Your Gut Health for Better Mental Wellness
- Eat a Diverse Diet: A diverse diet rich in fiber, prebiotics, and probiotics is essential for a healthy gut and a strong gut-brain connection.
- Reduce Stress: Stress management techniques such as meditation, yoga, and exercise can help maintain a healthy microbiome and reduce the negative effects of stress on the gut-brain connection.
- Avoid Antibiotics When Possible: Overuse of antibiotics can disrupt the balance of gut bacteria. Only take antibiotics when prescribed by your doctor.
- Consider Probiotics and Supplements: Probiotics can help restore the balance of your gut microbiome and improve your gut-brain connection, especially after illness or antibiotic use.
Conclusion
The gut-brain connection is a critical aspect of overall health. A healthy gut not only supports digestion but also enhances mental well-being, emotional stability, and cognitive function. By improving your diet and focusing on gut-friendly foods, you can boost your mental health and foster a balanced, resilient mind. Whether you’re dealing with stress, anxiety, or cognitive decline, nurturing the gut-brain connection through diet and lifestyle changes is a powerful step toward better mental health.
FAQ Section
Q1: Can gut health really affect mental health?
Yes, the gut-brain connection is vital for regulating mood, stress response, and cognitive function. An imbalance in the gut microbiome can lead to issues like depression and anxiety.
Q2: What foods are best for improving gut health?
Foods rich in prebiotics, probiotics, fiber, and omega-3 fatty acids are ideal for supporting the gut-brain connection. Examples include fermented foods, fruits, vegetables, fatty fish, and nuts.
Q3: How long does it take to see improvements in mental health by improving gut health?
It may take several weeks to a few months to see improvements in mood and mental health after dietary changes aimed at improving the gut-brain connection.
Q4: Can probiotics improve mental health?
Yes, probiotics can help restore balance to the gut microbiome, which has been shown to improve mood and alleviate symptoms of anxiety and depression.
Q5: Are there any foods I should avoid for better gut health?
Avoid processed foods, excessive sugar, and artificial sweeteners, as these can disrupt the gut-brain connection and negatively impact mental health.
Additional Resources:
- Harvard Health: The Gut-Brain Connection
- National Institutes of Health: Gut Microbiota and Mental Health
- Psychology Today: How the Gut Affects Your Mood
This updated version ensures that the focus keyword “Gut-Brain Connection” and its variations are well-integrated throughout the article for optimal keyword density while maintaining a natural flow and readability.





