"Discover how your gut health influences your mood and mental well-being. Explore 7 powerful ways the gut-brain connection can boost your mental clarity and emotional balance."
Meta Description:
“Discover the powerful connection between gut health and mental well-being. Learn how the gut-brain axis impacts mood, anxiety, and cognitive function, and explore tips to improve gut health for better mental clarity and emotional balance.”
The human body is an intricate network of systems that work together to maintain overall health and well-being. Among these systems, the gut and brain have a particularly special connection that plays a vital role in our mental health. The relationship between the gut and brain is known as the gut-brain axis, a two-way communication system that links the gastrointestinal tract with the central nervous system. In this article, we explore how gut health impacts mental well-being and how improving your gut health can lead to better emotional balance and cognitive function.
Understanding the Gut-Brain Axis
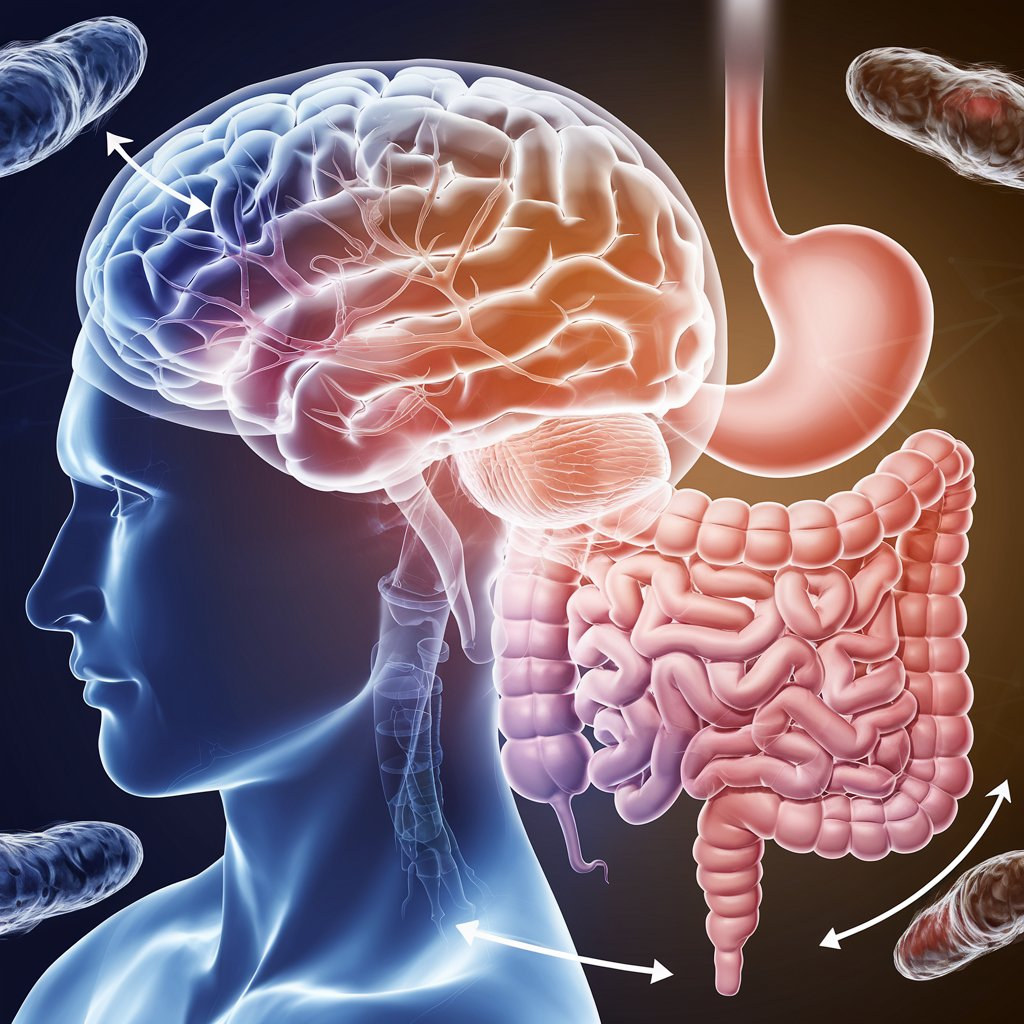
The gut-brain axis refers to the complex communication network between the gut and the brain. This connection is established via the vagus nerve, which acts as a major communication highway between the brain and the gastrointestinal system. Additionally, the gut houses a vast network of neurons, often referred to as the “second brain.” These neurons help regulate various processes in the body, including digestion, mood, and stress responses.
One of the most significant ways in which the gut influences the brain is through the production of neurotransmitters. For example, about 90% of serotonin, the “feel-good” neurotransmitter, is produced in the gut. Serotonin plays a critical role in regulating mood, anxiety, and happiness. A disruption in the gut’s ability to produce or process serotonin can contribute to mental health disorders such as depression, anxiety, and stress.
How Gut Health Impacts Mental Health

Research over the years has shown that the health of your gut can have a profound effect on your mental well-being. Here are some of the ways in which an imbalance in gut health can affect your mental health:
1. The Microbiome and Its Role in Mood Regulation
The gut is home to trillions of bacteria, collectively known as the gut microbiome. These microorganisms play a significant role in regulating brain function. An imbalance in the gut microbiome, known as dysbiosis, can lead to changes in mood, behavior, and cognitive function. Studies have shown that individuals with mental health disorders often have an imbalanced microbiome, with fewer beneficial bacteria and more harmful bacteria.
The gut microbiome affects the production of neurotransmitters, hormones, and inflammatory molecules. When the gut microbiome is disrupted, it can lead to the release of inflammatory cytokines that impact brain function, contributing to mental health issues like depression, anxiety, and even cognitive decline.
2. The Impact of Inflammation
Chronic inflammation, often originating in the gut, is another factor linking gut health to mental health. An unhealthy gut can trigger systemic inflammation, which can spread to the brain. This inflammation has been linked to several mental health conditions, including depression and anxiety. Inflammation in the brain can lead to changes in mood, cognitive function, and emotional regulation.
3. The Stress Connection
Stress can have a negative impact on gut health. Chronic stress can alter the gut microbiome, leading to an imbalance that contributes to digestive issues and mental health challenges. The gut-brain axis works in both directions: while stress can negatively impact the gut, poor gut health can also make the body more vulnerable to stress. This creates a vicious cycle that exacerbates both gut issues and mental health concerns.
How to Improve Gut Health for Better Mental Well-being

Fortunately, there are several ways to improve gut health, which, in turn, can have a positive impact on mental well-being. Here are some practical tips:
1. Eat a Diverse, Plant-Based Diet
A diet rich in fiber, fruits, vegetables, and whole grains provides the nutrients your gut bacteria need to thrive. The more diverse your diet, the more diverse your gut microbiome will be, which is associated with better mental and physical health. Include foods like oats, beans, lentils, leafy greens, and berries to feed beneficial gut bacteria.
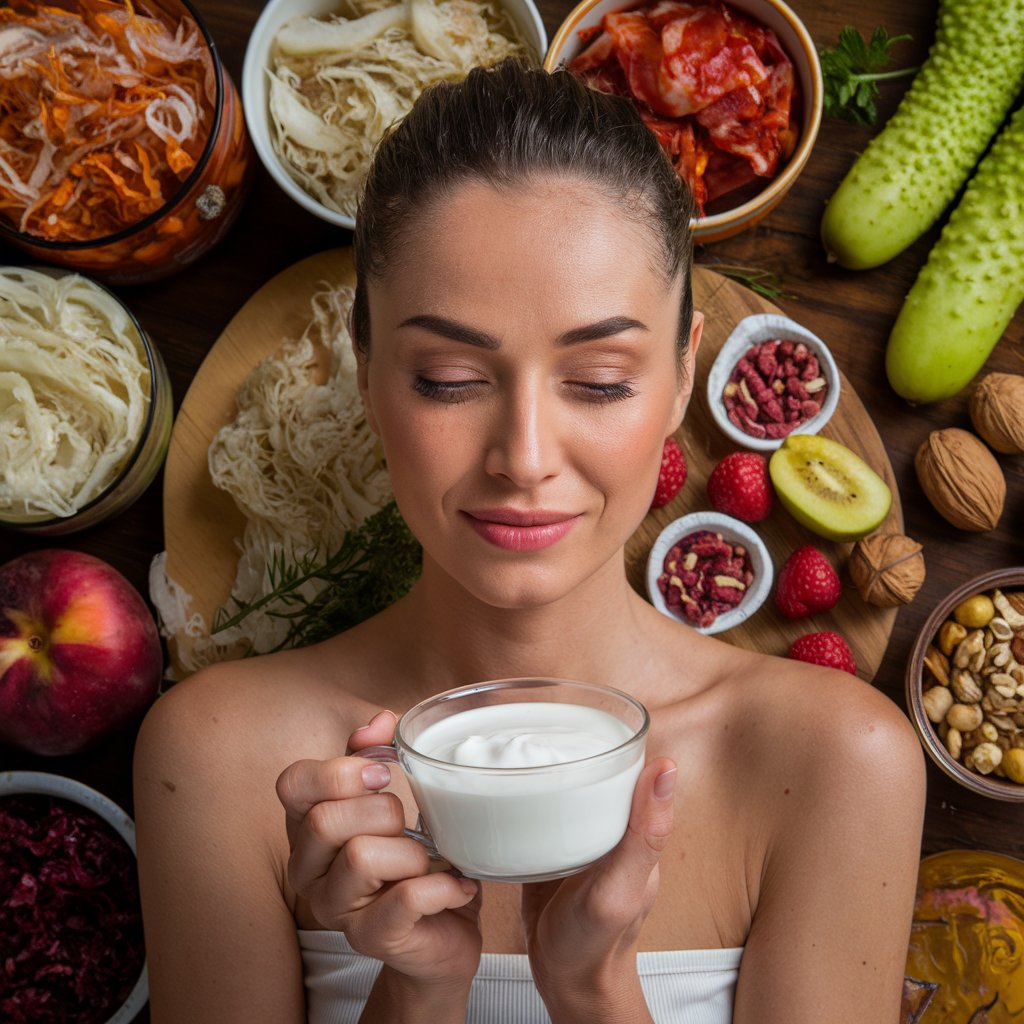
2. Include Probiotics and Fermented Foods
Probiotics are live bacteria that are beneficial to the gut. Incorporating probiotic-rich foods like yogurt, kefir, kimchi, sauerkraut, and kombucha into your diet can help replenish and diversify the beneficial bacteria in your gut, improving gut function and mental health. Probiotics can also help balance the gut microbiome and reduce inflammation.
3. Limit Processed Foods and Sugar
Diets high in processed foods, sugars, and unhealthy fats can promote an unhealthy gut microbiome. These foods can increase the growth of harmful bacteria and reduce the abundance of beneficial bacteria, leading to gut imbalances and inflammation. Avoiding or minimizing processed foods and refined sugars can help improve gut health and support better mental well-being.
4. Stay Hydrated
Drinking plenty of water is essential for maintaining proper gut function. Hydration supports the digestive system and helps facilitate the movement of nutrients and waste through the intestines. It also helps maintain a healthy balance of gut bacteria, which is essential for both physical and mental health.
5. Manage Stress Effectively
Since stress is a major factor that can disrupt both gut health and mental well-being, managing stress is crucial. Practices like mindfulness meditation, deep breathing exercises, yoga, and spending time in nature can help reduce stress and support gut health. Additionally, regular physical activity, such as walking or swimming, can improve both mental health and gut function.
6. Get Enough Sleep
Sleep is essential for both mental and physical health. Poor sleep can lead to gut imbalances and exacerbate mental health issues like anxiety and depression. Aiming for 7-9 hours of quality sleep each night can improve gut health and boost mood, cognitive function, and emotional regulation.
The Future of Gut Health and Mental Well-being

As research into the gut-brain connection continues to evolve, it is clear that maintaining a healthy gut is fundamental to supporting mental health. New therapies, such as microbiome-based treatments, are being explored to treat mental health disorders by targeting the gut microbiome. While the science is still unfolding, it’s clear that improving gut health through diet, lifestyle, and stress management can play a pivotal role in enhancing mental well-being.
Conclusion
The gut-brain connection is a fascinating and important aspect of overall health. By taking care of your gut, you can also take care of your mind. A healthy gut can lead to better emotional regulation, improved cognitive function, and a lower risk of mental health conditions like anxiety and depression. By making small changes to your diet, lifestyle, and stress management techniques, you can significantly improve both your gut and mental well-being, helping you lead a healthier, more balanced life.
FAQs for “Gut Health and Mental Well-being: The Brain-Gut Connection”
1. How does gut health affect mental well-being?
The gut produces a significant amount of neurotransmitters, like serotonin, that regulate mood and emotions. A healthy gut microbiome helps produce and balance these chemicals, contributing to better mental health and emotional stability.
2. Can poor gut health cause mental health issues?
Yes, an imbalance in the gut microbiome can lead to inflammation and disruptions in neurotransmitter production, contributing to conditions like anxiety, depression, and stress.
3. What are the signs of an unhealthy gut?
Signs of an unhealthy gut include digestive issues like bloating, gas, and constipation, as well as mood swings, fatigue, skin problems, and frequent illnesses.
4. How can I improve my gut health for better mental well-being?
Improving gut health involves a balanced diet rich in fiber, fermented foods, and probiotics, while reducing processed foods and managing stress through practices like mindfulness and regular exercise.
5. Does stress affect gut health?
Yes, chronic stress can disrupt the gut microbiome, leading to digestive problems and negatively impacting mental health. Stress management is key to maintaining both gut health and emotional well-being.
6. Is there a link between gut health and anxiety or depression?
Yes, an imbalanced gut microbiome can influence brain function and emotional regulation, leading to symptoms of anxiety, depression, and other mood disorders.
7. How long does it take to improve gut health?
It can take several weeks to months of consistent dietary and lifestyle changes to see significant improvements in gut health, but many people begin to feel better within a few weeks.
8. Can probiotics help with mental health?
Some studies suggest that certain probiotics may help alleviate symptoms of anxiety and depression by restoring balance to the gut microbiome and reducing inflammation.
9. Is there a specific diet that supports both gut and brain health?
A diet rich in fiber, fruits, vegetables, and fermented foods like yogurt and kefir supports gut health, which in turn benefits brain function and mental well-being.
10. Can gut health be restored naturally?
Yes, restoring gut health naturally involves dietary changes, stress management, hydration, and physical activity. These lifestyle adjustments can significantly improve both gut and mental health.





